Example - Building a Custom Basemap through Styling - Part 2
Learn how to create a custom Game of Thrones basemap with Builder.
Resources
*All thematic data was built from the gvSIG’s ebook, Learning GIS with Game of Thrones. Textures and icons were created from Textures and The Noun Project websites.
Getting started
- Import the template .carto file to your account.
- Open the map.
- Rename your map as Game of Thrones Basemap.
- Make sure that the order and names of your layers are as follows:
locations> Locationswall> The Ice Wallpolitical> Regionsrivers_and_roads> Rivers and roadsmountains_lakes> Mountains and lakespolitical> Beyond the Wallcontinents_and_islands> Continents and islandscontinents_and_islands> Ripples
Ocean and ripples
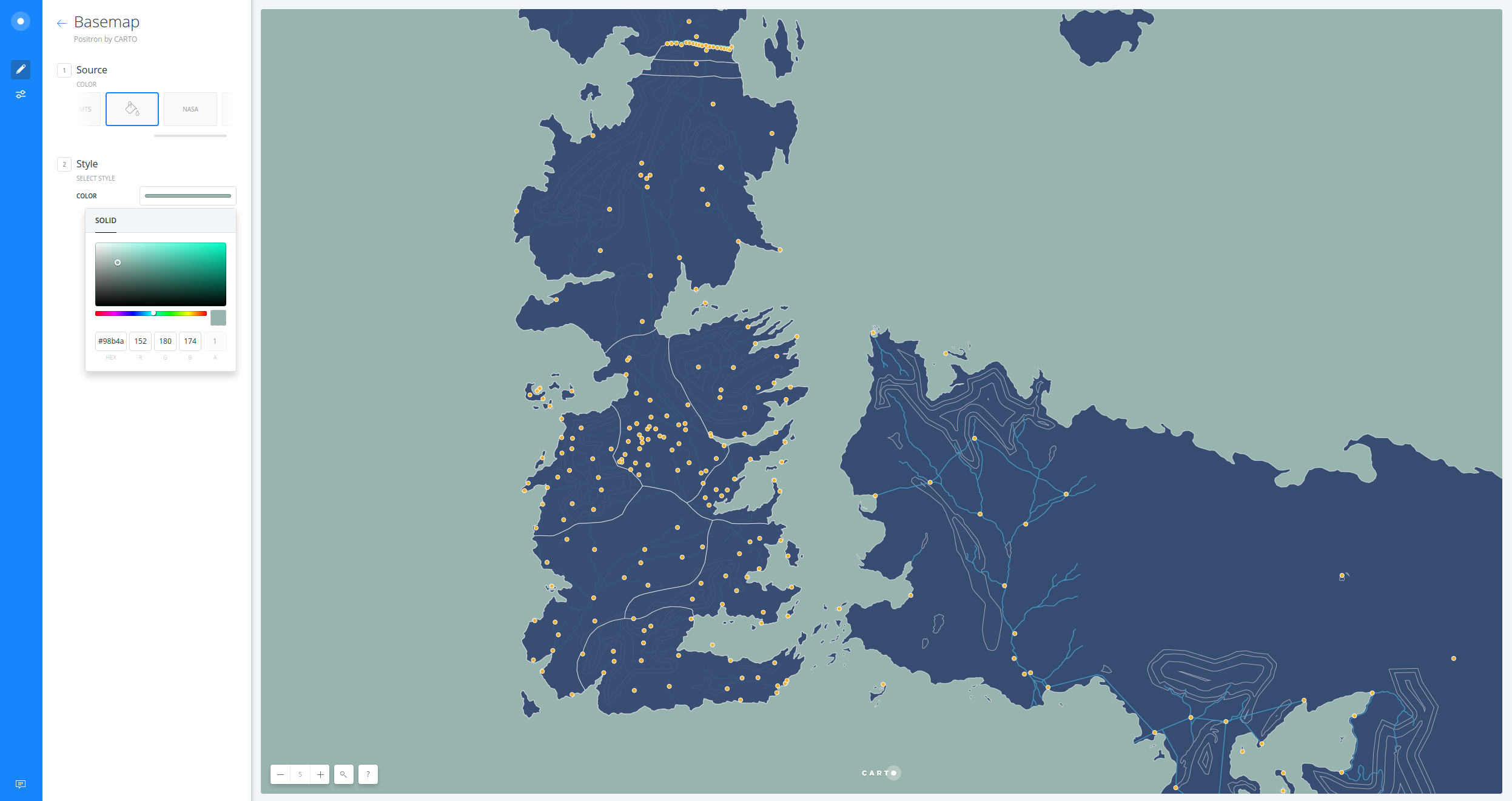
- First, change the basemap:
- Click on the Positron basemap
- Select
COLOR - Replace the default color with
#98b4ae
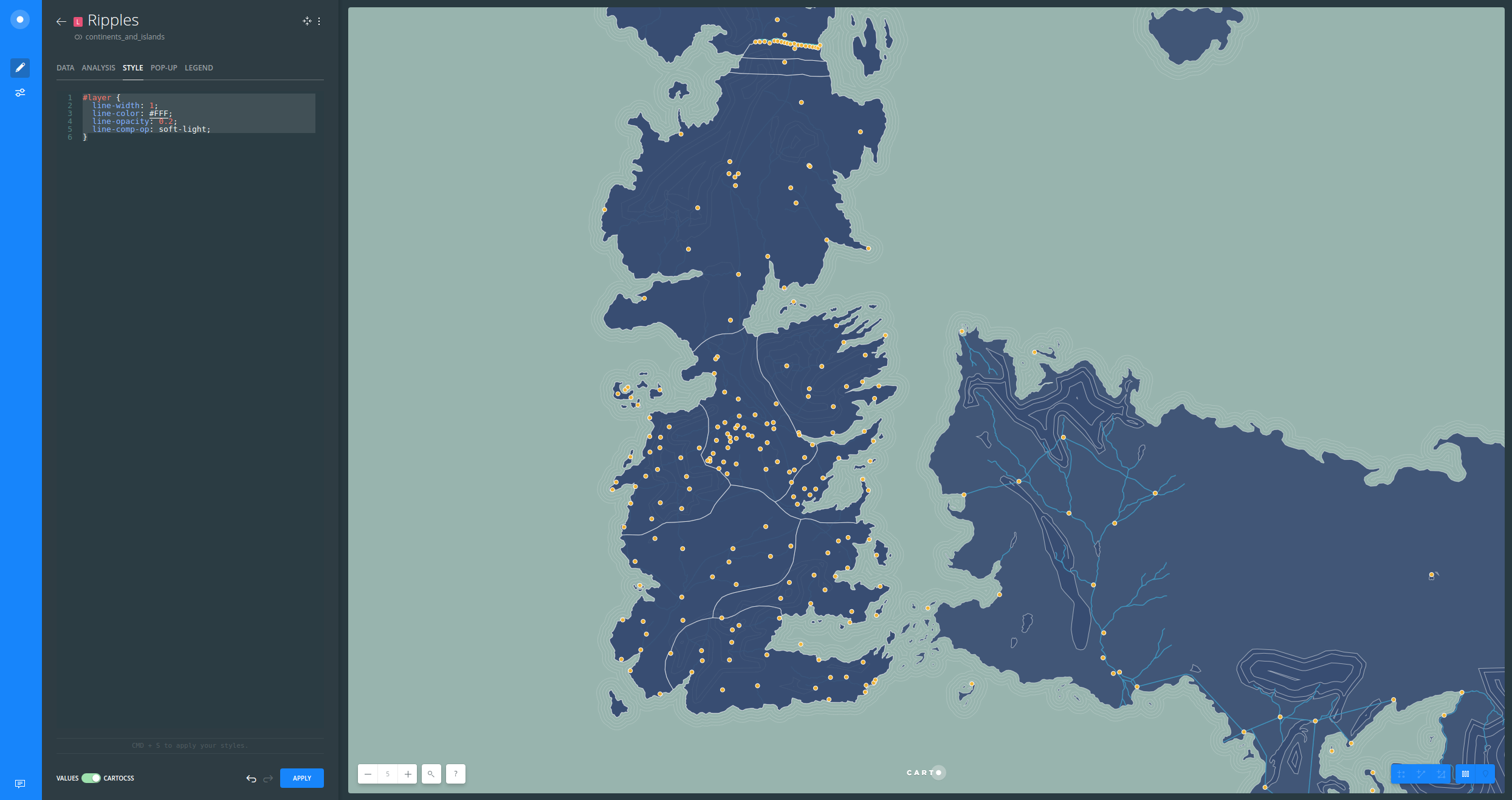
- In order to create a coastal ripple effect, follow these instructions:
- Click on the Ripples layer and go to the ANALYSIS tab
- Click on ADD ANALYSIS button to add a new analysis
- Select Create Areas of influence
- Click on ADD ANALYSIS
- Set the parameters as follows:
- TYPE:
Distance - UNITS:
mi(miles) - RADIUS:
60 - TRACTS:
4 - BOUNDARIES:
Dissolve(try to useIntact!)
- TYPE:
- Click APPLY
- Go to the STYLE tab and switch from VALUES to CARTOCSS
- Replace the default style with the following one:
#layer {
line-width: 1;
line-color: #FFF;
line-opacity: 0.2;
line-comp-op: soft-light;
}
soft-lightcomposite operation will soften the parts where two lines overlap when unsingIntactbuffers.
- Click APPLY
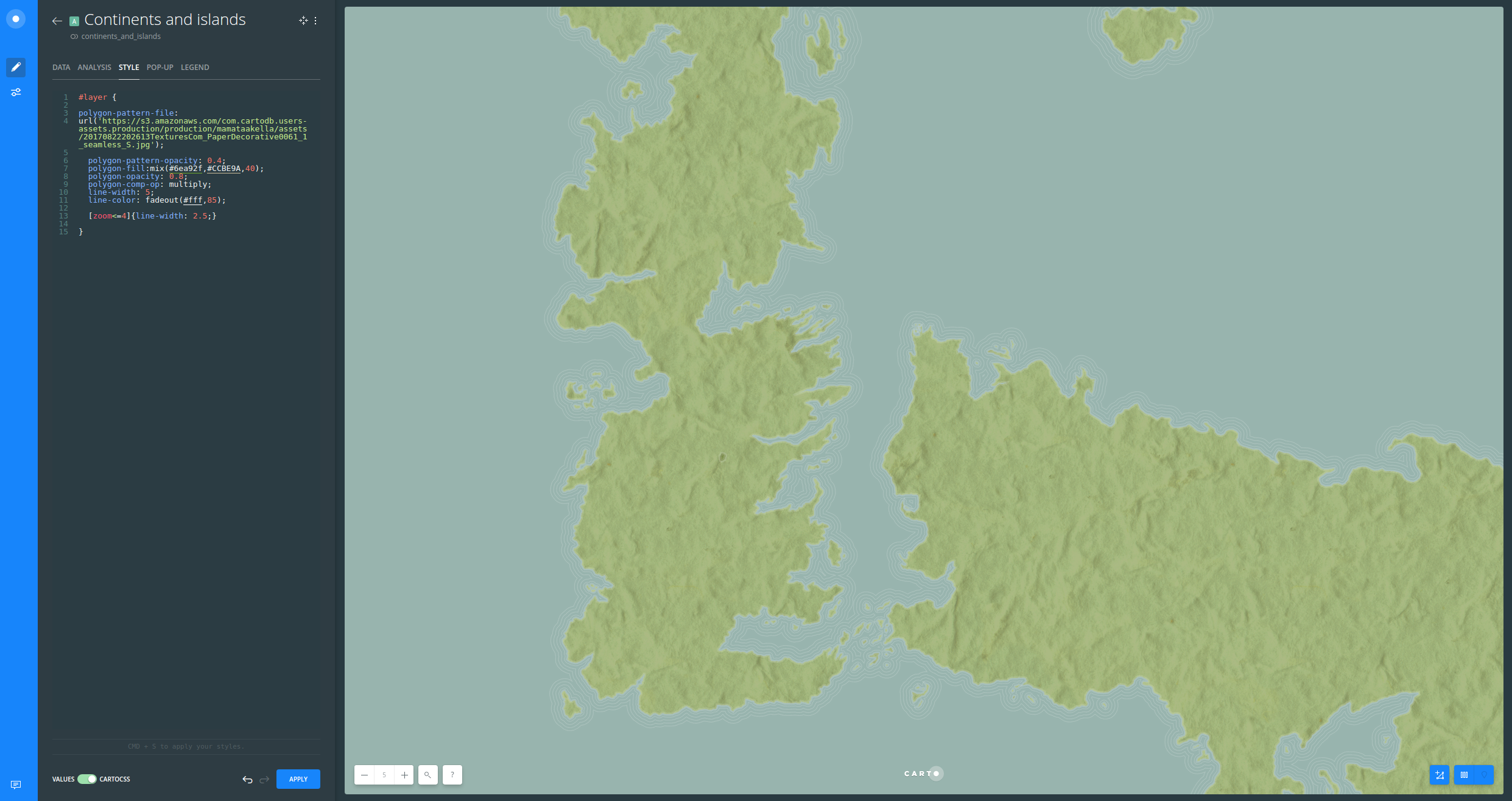
Continents and islands
- Hide all layers from your Map View except for Continents and islands
- In order to style the land, follow these steps:
- Click on Continents and islands layer
- Switch from VALUES to CARTOCSS
- Replace the default style with the following:
#layer {
polygon-pattern-file:
url('https://s3.amazonaws.com/com.cartodb.users-assets.production/production/mamataakella/assets/20170822202613TexturesCom_PaperDecorative0061_1_seamless_S.jpg');
polygon-pattern-opacity: 0.4;
polygon-fill:mix(#6ea92f,#CCBE9A,40);
polygon-opacity: 0.8;
polygon-comp-op: multiply;
line-width: 5;
line-color: fadeout(#fff,85);
[zoom<=4]{line-width: 2.5;}
}
As you can see, the pattern we have given to the land has a feeling of rugosity. Also, mixing two colors in the
polygon-fillproperty and usingfadeoutto simulate the end of the land masses are good cartography tricks.
- Click APPLY
Mountains and lakes
- Show the Mountains and lakes layers from the Map View
- Again, follow these instructions to style this layer:
- Click on Continents and islands layer
- Switch from VALUES to CARTOCSS
- Replace the default style with the following:
#layer [type = 'mountain']{
polygon-pattern-file: url('https://s3.amazonaws.com/com.cartodb.users-assets.production/production/mamataakella/assets/20170823212836mountain-range.png');
polygon-pattern-opacity: 0.3;
}
#layer[type='lake'] {
polygon-fill: #718c9f;
polygon-opacity: 0.7;
line-width: 1;
line-color: rgba(255,255,255,0.1);
}
#layer[type='swamp']{
polygon-opacity: 0.4;
polygon-fill: mix(#6ea92f,#718c9f,30);
}
We are using a pattern with a grid of mountain icons to emulate mountain ranges. In addition, swamps were colored mixing water and ground colors.
- Click APPLY
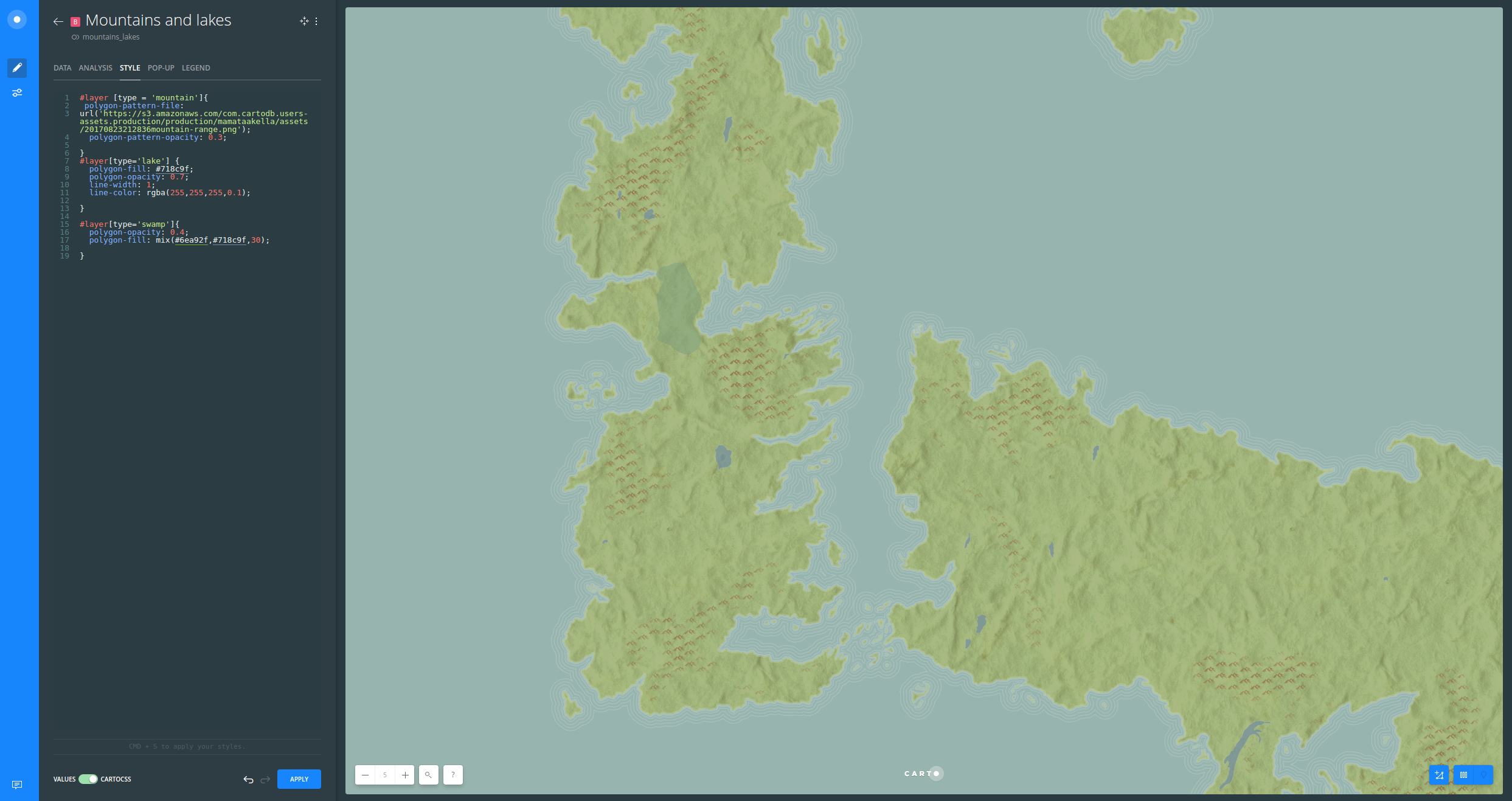
Rivers and roads
- Enable the view from the Rivers and roads layer
- Follow these instructions to style this layer:
- Click on Rivers and roads layer
- Switch from VALUES to CARTOCSS
- Replace the default style with the following:
#layer {
[type='river']{
line-width: 1;
line-color: #718c9f;
line-opacity: 0.9;
[zoom<=4]{line-width: 0.5;}
[zoom>=6]{line-width: 1.5;}
}
[type='road']{
::case {
line-width: 4;
line-color: #3b3b3b;
line-opacity: 0.3;
[zoom<=4]{line-width: 0;}
[zoom>=6]{line-width: 5;}
}
::fill{
line-width: 2;
line-color: lighten(#8C9F71,10);
line-opacity: 0.9;
[zoom<=4]{line-width: 0;}
[zoom>=6]{line-width: 3;}
}
}
}
Rivers and roads were styled based on zoom.
- Click APPLY
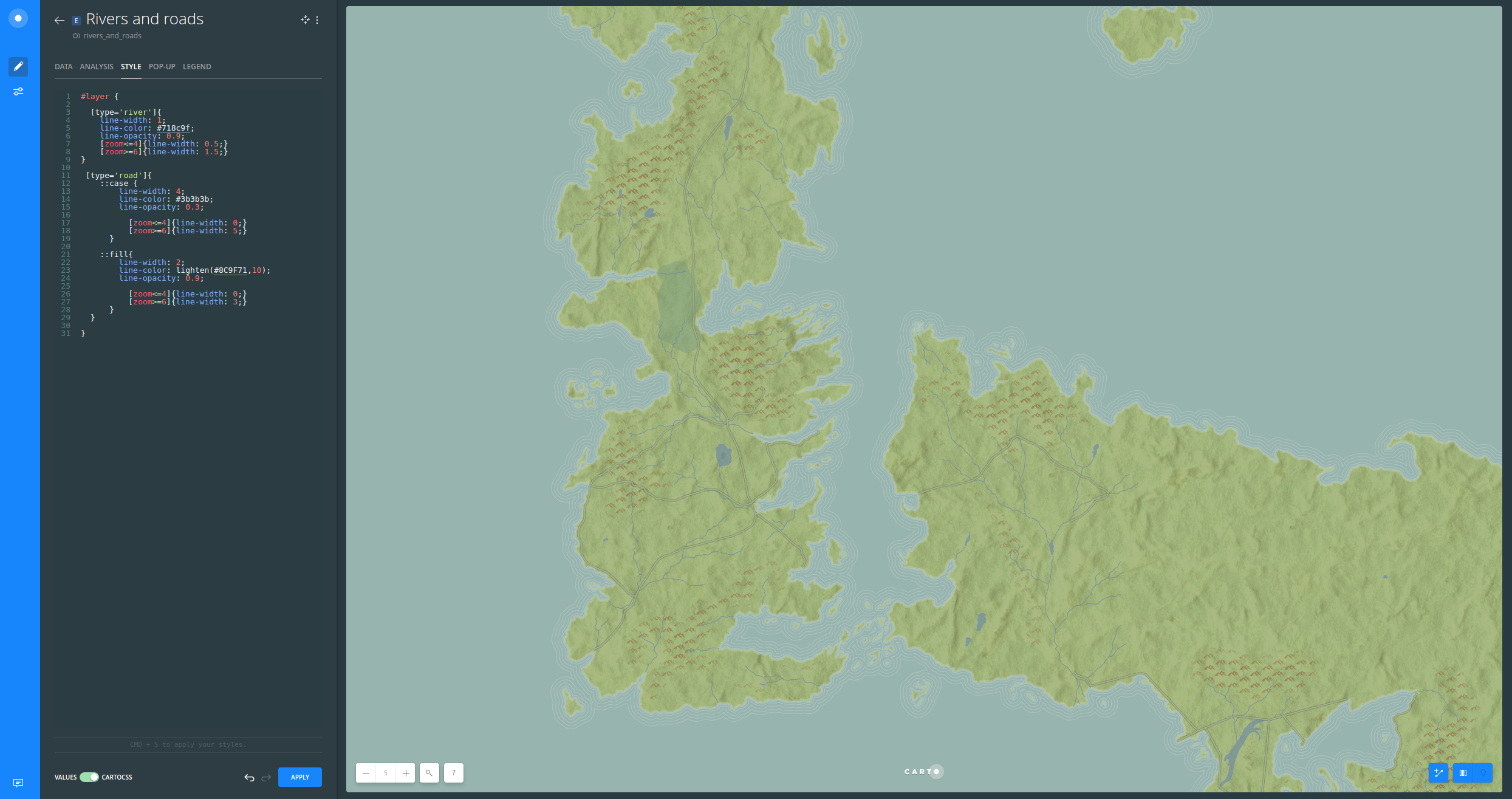
The Ice Wall and beyond
- In order to create a 2.5D effect, follow these instructions:
- Click on the The Ice Wall layer and go to the ANALYSIS tab
- Click on ADD ANALYSIS button to add a new analysis
- Select Create Areas of influence
- Click on ADD ANALYSIS
- Set the parameters as follows:
- TYPE:
Distance - UNITS:
km(kilometers) - RADIUS:
9 - TRACTS:
1 - BOUNDARIES:
Intact
- TYPE:
- Click APPLY
- Go to the STYLE tab and switch from VALUES to CARTOCSS
- Replace the default style with the following:
#layer {
line-width: 0.25;
line-color: #FFF;
line-opacity: 0.5;
building-fill: #ffffff;
building-fill-opacity: 1;
building-height: 55000;
}
The 2.5D effect was made because of the
buildingproperties. Check CartoCSS documentation for more detailed information about this method.
- Click APPLY
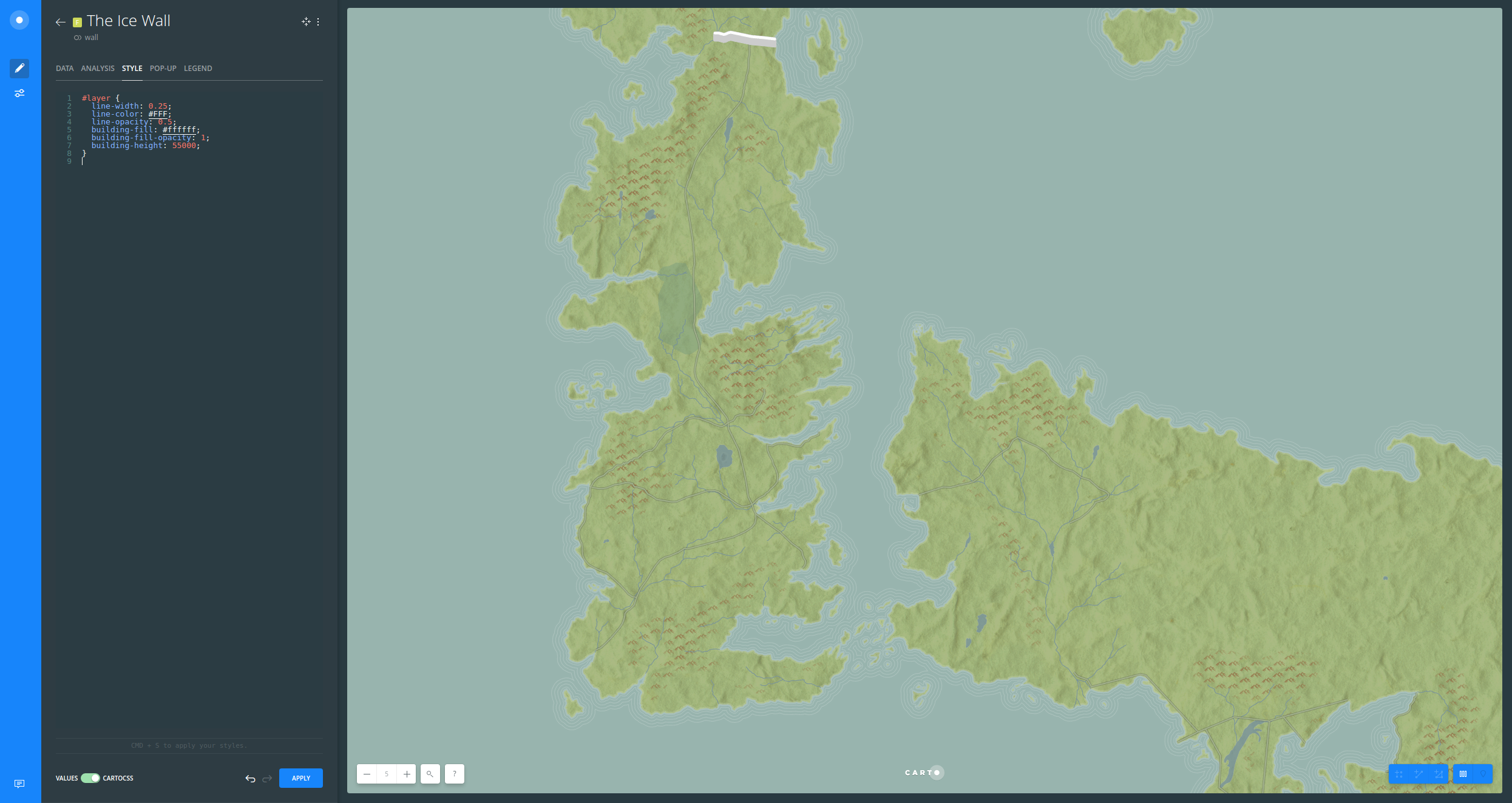
- Show the Beyond the Wall layer from the Map View
- Again, follow these instructions to style this layer:
- Click on Beyond the Wall layer
- Switch from VALUES to CARTOCSS
- Replace the default style with the following:
#layer[cartodb_id=3] {
polygon-fill: #fff;
polygon-opacity: 0.65;
}
- Click APPLY
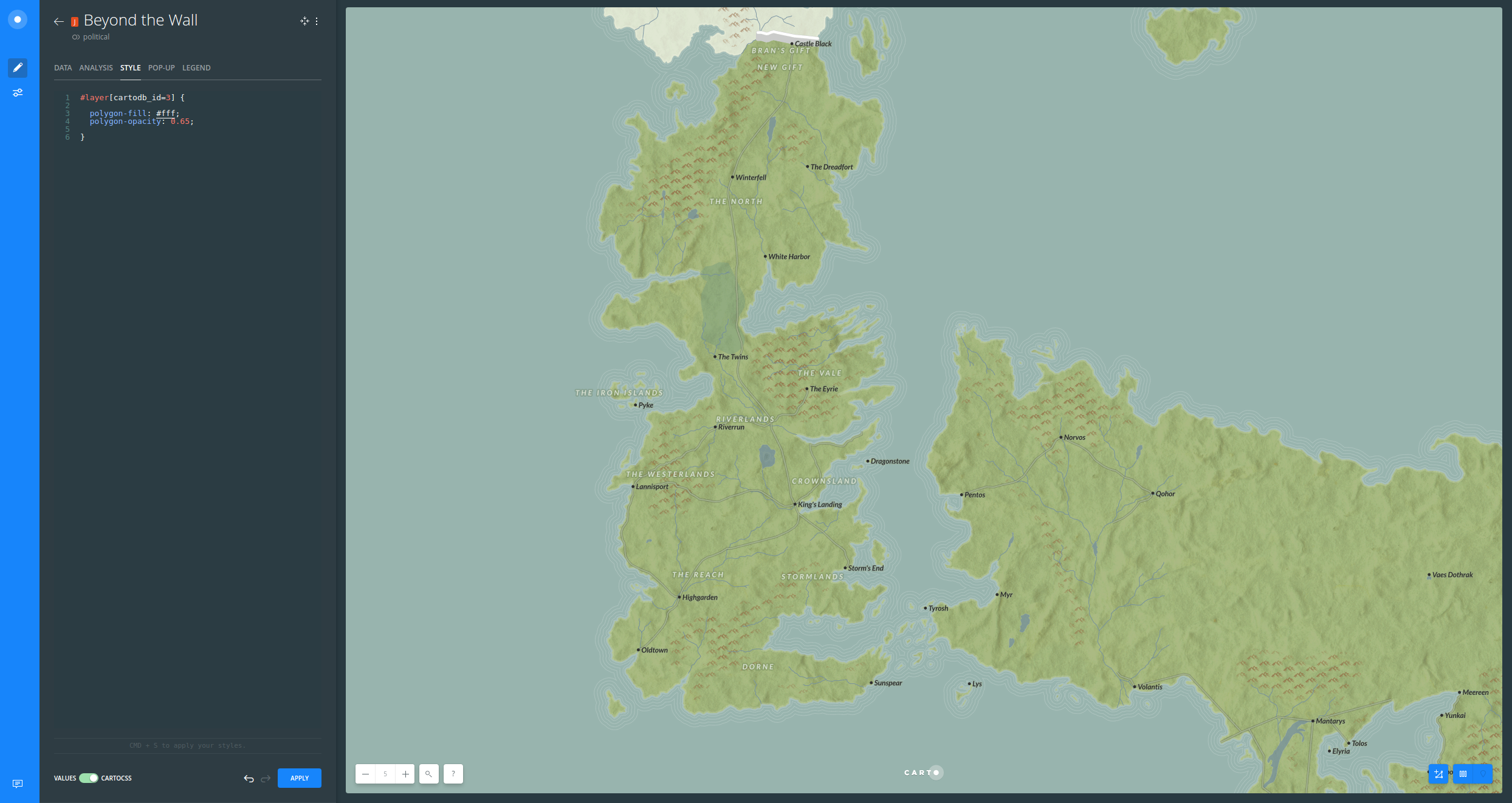
Regions and towns
- Show the Locations layer from the Map View
- Follow these instructions to style this layer:
- Click on Locations layer
- Switch from VALUES to CARTOCSS
- Replace the default style with the following:
Map{
buffer-size: 512;
}
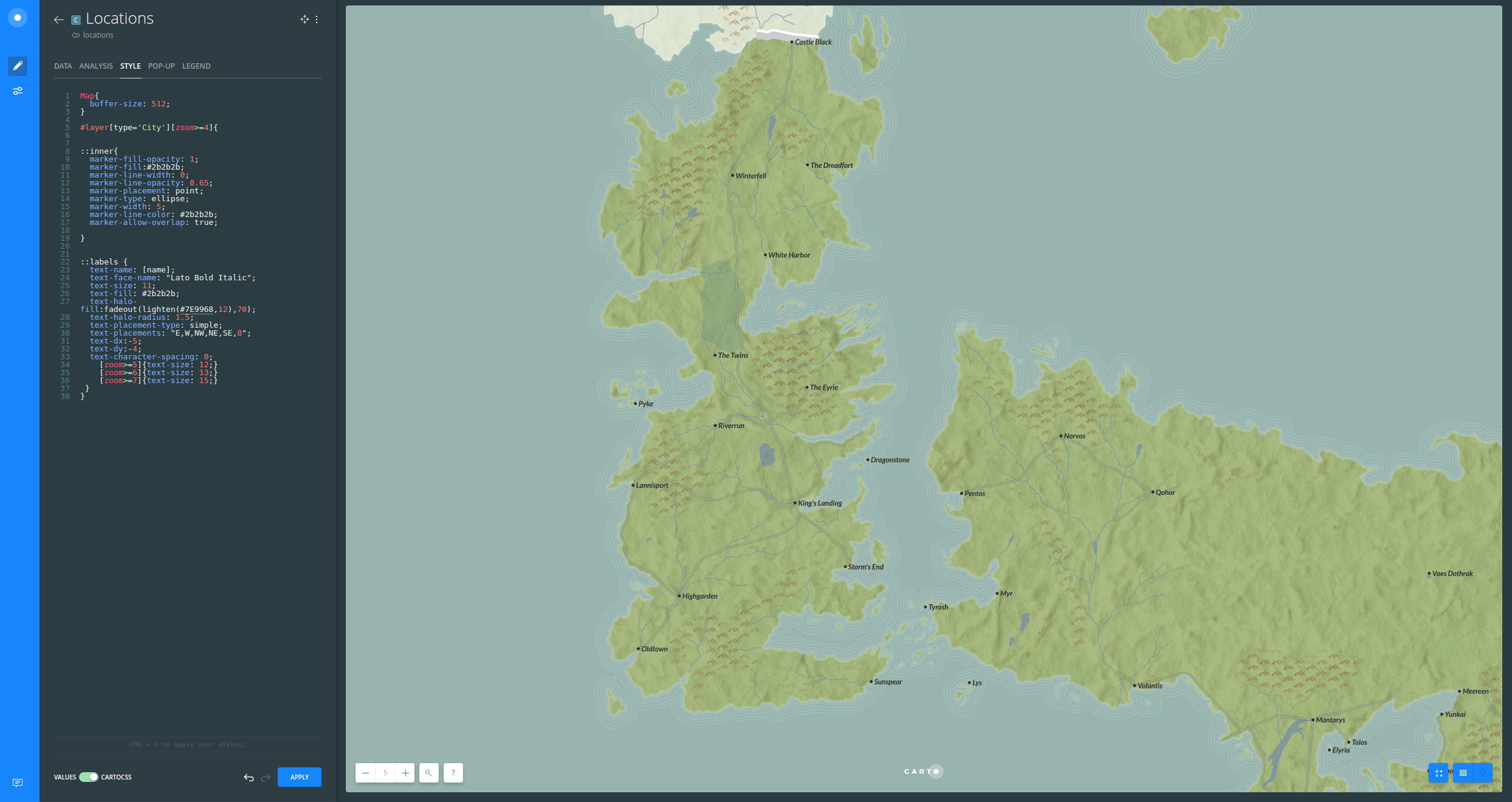
#layer[type='City'][zoom>=4]{
::inner{
marker-fill-opacity: 1;
marker-fill:#2b2b2b;
marker-line-width: 0;
marker-line-opacity: 0.65;
marker-placement: point;
marker-type: ellipse;
marker-width: 5;
marker-line-color: #2b2b2b;
marker-allow-overlap: true;
}
::labels {
text-name: [name];
text-face-name: "Lato Bold Italic";
text-size: 11;
text-fill: #2b2b2b;
text-halo-fill:fadeout(lighten(#7E9968,12),70);
text-halo-radius: 1.5;
text-placement-type: simple;
text-placements: "E,W,NW,NE,SE,8";
text-dx:-5;
text-dy:-4;
text-character-spacing: 0;
[zoom>=5]{text-size: 12;}
[zoom>=6]{text-size: 13;}
[zoom>=7]{text-size: 15;}
}
}
Location labels are also styled based on zoom. Labels work nicely because of the font, size, halo and placement.
- Click APPLY
- Show the Locations layer from the Map View
- Follow these instructions to style this layer:
- Click on Locations layer
- Switch from VALUES to CARTOCSS
- Replace the default style with the following:
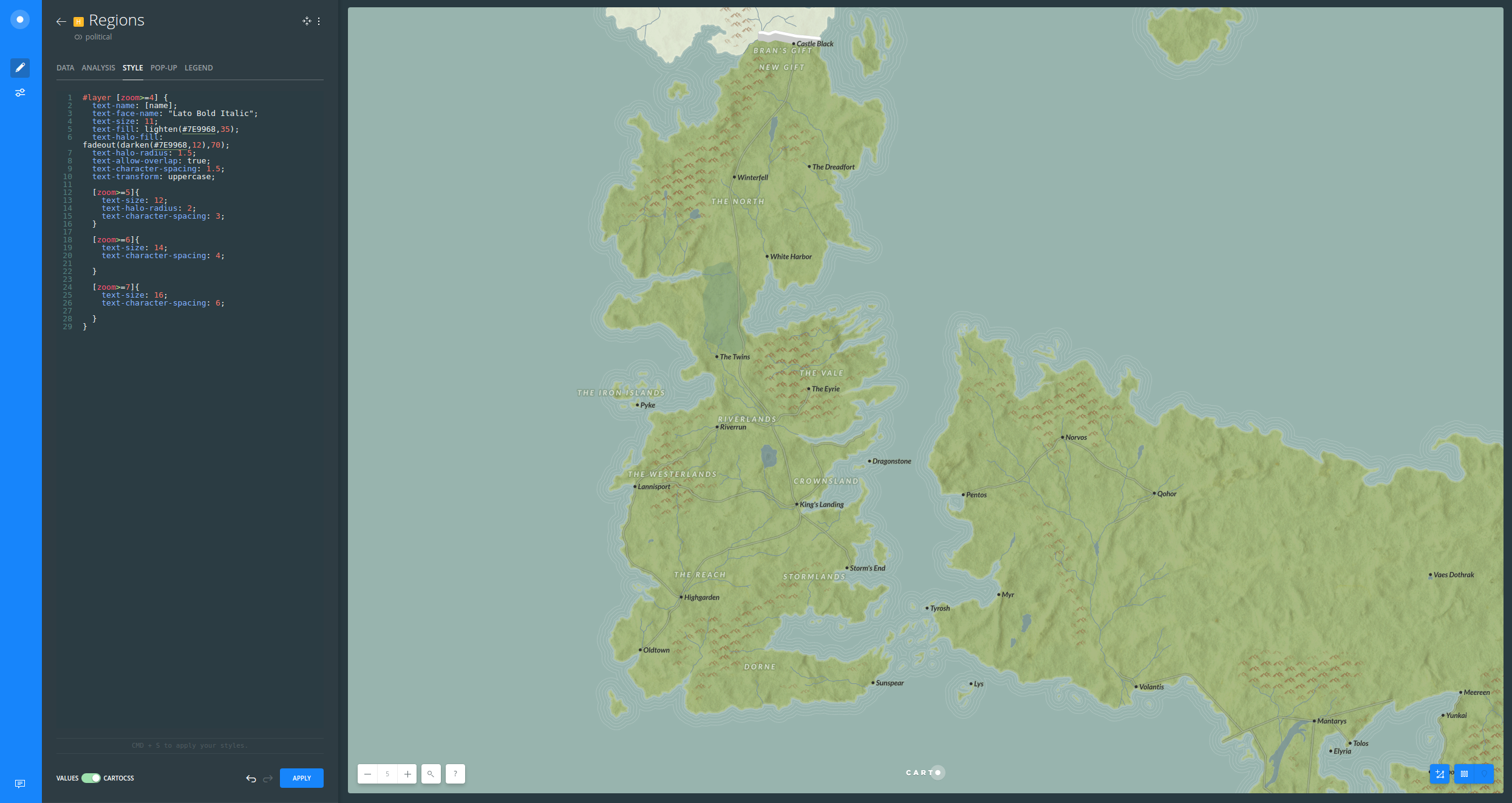
#layer [zoom>=4] {
text-name: [name];
text-face-name: "Lato Bold Italic";
text-size: 11;
text-fill: lighten(#7E9968,35);
text-halo-fill: fadeout(darken(#7E9968,12),70);
text-halo-radius: 1.5;
text-allow-overlap: true;
text-character-spacing: 1.5;
text-transform: uppercase;
[zoom>=5]{
text-size: 12;
text-halo-radius: 2;
text-character-spacing: 3;
}
[zoom>=6]{
text-size: 14;
text-character-spacing: 4;
}
[zoom>=7]{
text-size: 16;
text-character-spacing: 6;
}
}
Regions were styled based upon zoom, similar to how location labels were styled. A very cool effect is giving some spaces between the word characters and transforming them into
uppercase.
- Click APPLY
You know nothing!
- Share your map following these instructions:
- Click on SHARE
- Click on PUBLISH
a. Share the URL of your map:
https://public.carto.com/builder/d6700550-7314-434f-9691-0645d86c7cc3/embedb. Embed the iframe into your website:
<iframe width="100%" height="520" frameborder="0" src="" allowfullscreen webkitallowfullscreen mozallowfullscreen oallowfullscreen msallowfullscreen></iframe>
- As a bonus, we are going to convert this Builder map into a basemap. This will allow us to put on top character thematic data:
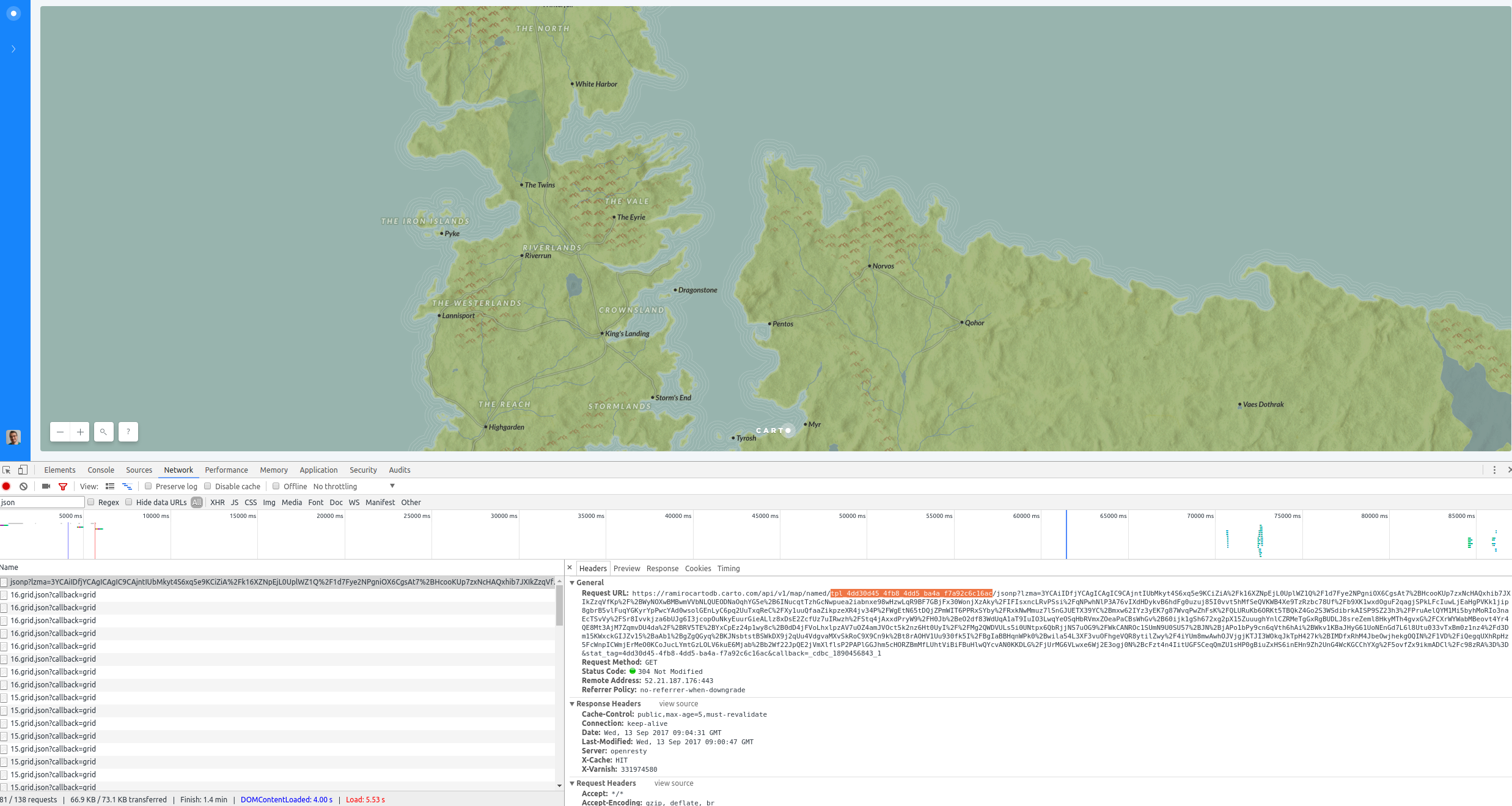
- Open the
Networktab from your browser developer tools console. - Look for the call that starts with
jsonand get the template id from theRequest URL:
- Open the
iii. Replace your user name and template id in the following URL:
https://http://cartocdn-gusc.global.ssl.fastly.net/USERNAME/api/v1/map/named/TEMPLATE_ID/all/{z}/{x}/{y}.png
iv. You will end up with a URL similar to this one:
https://cartocdn-gusc.global.ssl.fastly.net//ramirocartodb/api/v1/map/named/tpl_756aec63_3adb_48b6_9d14_331c6cbc47cf/all/{z}/{x}/{y}.pngg
- Finally, you can add this custom basemap following this guide.